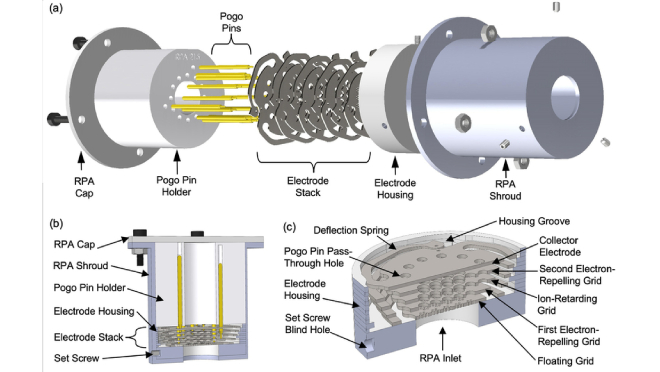
In an effort to ease weather estimates and climate change, scientists in MIT have developed a plasma sensor that is fully produced to orbit a spacecraft. Satellite uses this plasma sensor, also known as Retaching Potential Analyzer (RPA), to determine the chemical composition of the atmosphere and ion energy distribution.
3D print sensors for satellites are durable and appropriate sensors that can be used effectively on low and light -cost satellites known as cubesats, which are usually used for environmental monitoring or weather forecasting.
This research work was led by Luis Fernando Velásquez-Garcia, a major scientist at MIT’S Microsystems Technology Laboratories (MTL), and research colleagues including the main writer and Postdoc MTL Javierdo-Reyes, Zoey Bigew graduation students, and Postdoc Nicholas K. . This study was published in the journal Additive Manufacturing.
RPA is made by researchers using glass ceramic materials that are more durable than traditional sensor materials such as silicon and thin film coating. They are able to make sensors with complex shapes that can withstand a wide temperature swing that will be found by spacecraft in the lower ground orbit using glass ceramics in the fabrication process developed for 3D printing with plastic.
The hardware printed 3D and laser carried out as well as sophisticated semiconductor plasma sensors produced in a clean room, which is expensive and takes weeks to finish it. In comparison, 3D printed sensors can be produced in a matter of days for tens of dollars.
Speaking of new development, the main writer, Luis Fernando Velásquez-García, said that once someone wanted to innovate, one must be willing to fail and accept the risk. Additive manufacturing is a very different method in producing space hardware.
In his words: “If you want to innovate, you must be able to fail and pay the risks. Additive manufacturing is a very different way to make space hardware. I can make room hardware and if it fails, it’s not a problem because I can make a new version very quickly and cheaply, and turn to the design. This is the ideal sand box for researchers. “
However, he added, “Manufacturing additives can make big differences in the future of space hardware. Some people think that when you print 3D something, you have to admit less performance. But we have shown that it is not always the case. Sometimes there is nothing to be traded.


![Scientists are turning dead spiders into robots, the tech is called ‘necrobotics’ [WATCH]](https://highonwing.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/93155021-150x150.webp)


![Scientists are turning dead spiders into robots, the tech is called 'necrobotics' [WATCH]](https://highonwing.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/93155021-300x169.webp)